Overview
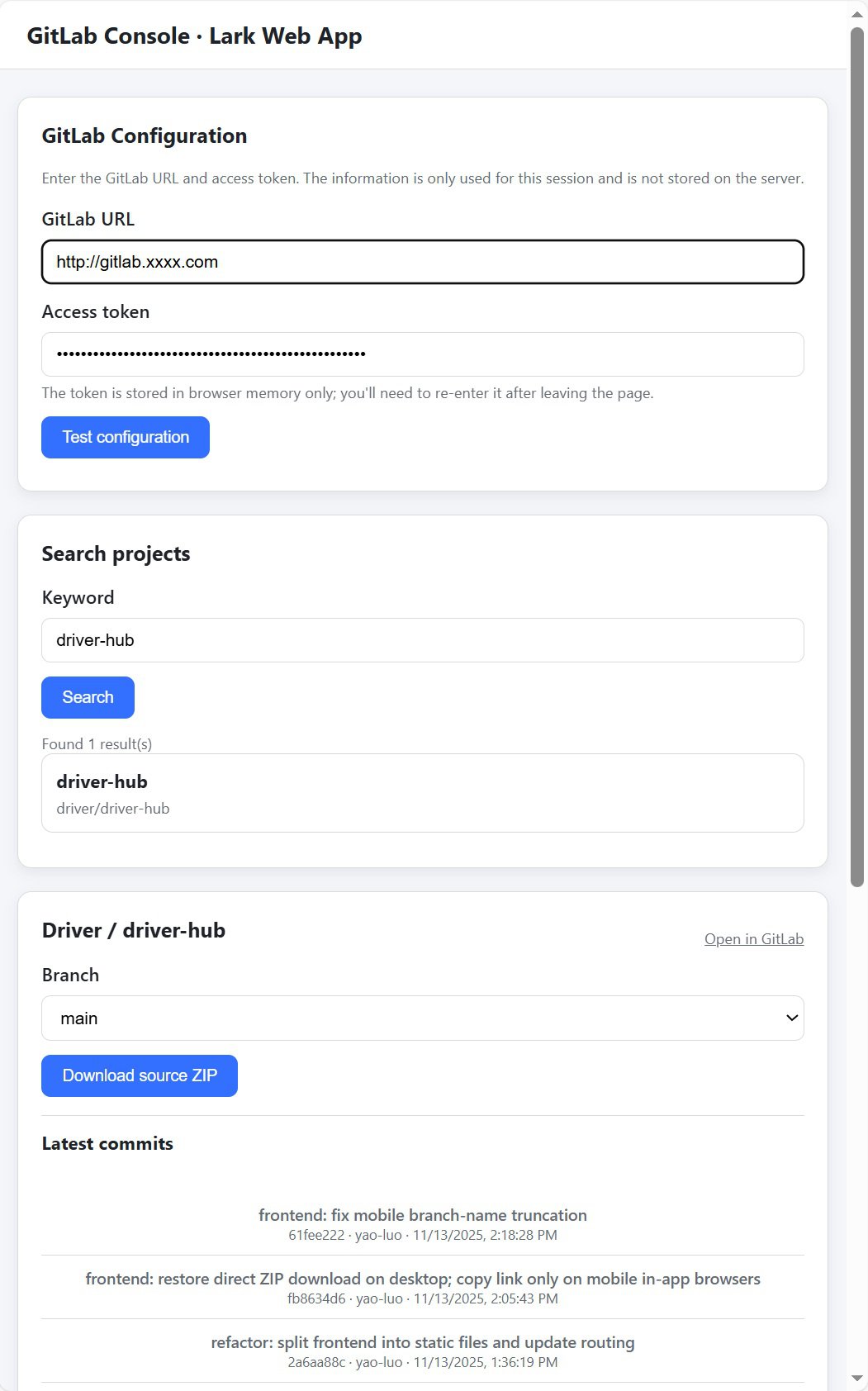
This article introduces Driver-Hub, a Feishu (Lark) Web Application I built to connect with our internal GitLab server.
The app allows searching projects, browsing branches, viewing commits, and downloading code archives directly from Feishu’s workplace UI.
The implementation is purely web-based.
Traditional bot features were removed — users open Driver-Hub in Feishu, interact with form controls, and the app communicates with GitLab APIs through FastAPI.
1. Feishu Developer Platform Setup
Before writing any code, configure a Feishu developer app to host the Driver-Hub UI.
Step 1. Create a New Application
- Go to your organization’s Feishu Developer Console.
- Click Create App → select Internal Application.
- Enter the name
Driver-Hub, add an icon and description. - Save and note your App ID and App Secret.
Step 2. Enable Web Application
- Left sidebar → Functional Configuration → Web Application.
- Enable “Workplace Web Application”.
- Fill homepage URLs (desktop & mobile):
https://<your-ngrok-domain>/ - Save the configuration.
Step 3. Publish the Application
After setup, go to Version Management & Release → Release → “Only visible to me”.
Then open Feishu → “Workplace” → find Driver-Hub → open the embedded page.
2. Running a Local HTTPS Endpoint with ngrok
Feishu requires a public HTTPS endpoint for embedded web pages.
Instead of deploying to the cloud, we use ngrok to expose FastAPI (localhost:3000) securely.
Step 1. Install ngrok
Using Scoop on Windows:
scoop install ngrok
Or macOS Homebrew:
brew install ngrok/ngrok/ngrok
Step 2. Connect Your Account
After signing up at https://ngrok.com:
ngrok config add-authtoken <YOUR_AUTHTOKEN>
Step 3. Start the Tunnel
ngrok http 3000
Output example:
Forwarding https://driverhub.ngrok-free.dev -> http://localhost:3000
Use this HTTPS address in Feishu’s web app config.
⚠️ Free-tier ngrok adds a browser warning page that blocks Feishu WebView.
For stable use, upgrade ngrok or deploy Driver-Hub on an internal HTTPS server.
3. GitLab Personal Access Token
Driver-Hub communicates with GitLab via its REST API, requiring a Personal Access Token (PAT).
Step 1. Create Token
- Log in to your GitLab (e.g.,
https://gitlab.xxx.net). - Go to Preferences → Access Tokens.
- Set:
- Name:
driver-hub - Scopes:
api,read_repository
- Name:
- Click Create Token, then copy it (only shown once).
Step 2. Test the Token
curl --header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: <your_token>" https://gitlab.xxx.net/api/v4/user
Should return user info JSON.
4. FastAPI Backend
main.py serves both UI and REST endpoints.
| Endpoint | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
/ | GET | Serve main HTML UI |
/api/config/test | POST | Validate GitLab base URL and token |
/api/projects | GET | Search GitLab projects |
/api/projects/{id}/branches | GET | List branches |
/api/projects/{id}/commits | GET | List commits |
/api/projects/{id}/branches/{branch}/archive | GET | Download ZIP |
Example route:
@app.get("/")
def index():
return "<h2>Driver-Hub Web UI is running</h2>"
5. Run the Application
Start FastAPI locally:
python main.py
Then start ngrok:
ngrok http 3000
Open Feishu → “Workplace” → Driver-Hub → view the web UI.
6. Summary
Driver-Hub is a lightweight internal GitLab management console embedded directly inside Feishu.
It uses Python + FastAPI for backend logic, ngrok for HTTPS tunneling, and GitLab’s REST API for project operations.
For production, host Driver-Hub on an internal server with HTTPS, e.g. https://driver-hub.xxx.net.
Project Structure
.
├── main.py
├── gitlab_client.py
├── favicon.ico
└── .env